Ice cream, apple pie, and chocolate… Sugar is tasty, but it’s also claimed to be unhealthy. So, can you live without sugar?
Can you live without sugar?
I suffer from diabetes. I have dysfunctional insulin production and have to balance the sugar intake with injected insulin. The body of a non-diabetic regulates this by itself, but I need to take injections.
The principle is the same though… The more sugar, the more insulin, injected or naturally produced. So, I started wondering, why all this fuss about it, about the sugar? Why not just throw it out altogether, the apple pies, and the ice cream… Why not completely stop eating sugar, and my blood sugar values would be under control…
And I wondered… Is it possible? Can you live without sugar?
- Disclaimer: I am not a scientist, nor a medical expert. Before trying any radical diet, please consult your primary care provider
Sugar is the fuel for the human organism.
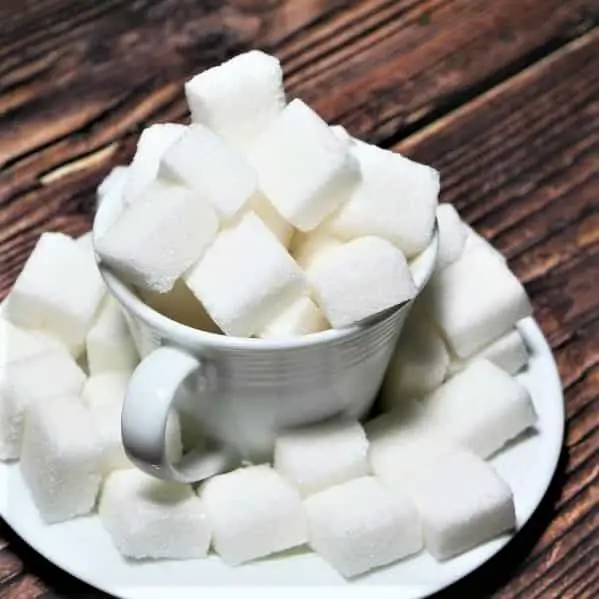

Sugar is a generic name for soluble, sweet carbohydrates. Any carb with only one or two sugar molecules will taste sweet and is called sugar. All carbohydrates, one, two, or more molecules, are our body’s main source of energy. We need them to move, think, and all the rest. Without carbs, we would still survive because of backup systems like ketosis, where fat is used for energy. But, in the long run, with no carbs, you will face health issues. More about that further ahead.
Sugar – A chemical definition.
So, can you live without sugar? Yes of course you can, if you’re Ok with sacrificing grandma’s brownies. But the real question should be, can you live completely without carbohydrates? That is, without any bread, potatoes, rice, beans, fruit, etc..
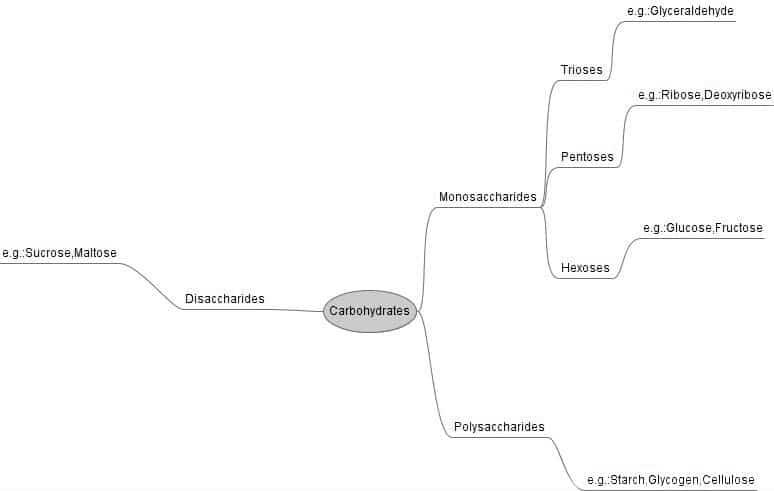
A very simplified way to explain the complex system of carbohydrates is this:
There are three monosaccharides, single-molecule carbohydrates. These are glucose, fructose, and galactose. These three contain the building blocks, and they are very sweet, especially glucose. If you put two of these molecules together, you get a disaccharide, e.g. normal table sugar (sucrose) which is one glucose molecule and one fructose molecule. Sucrose is produced from processing Sugarcanes or sugar beets and these disaccharides are still very sweet.
Combining more molecules you get oligosaccharides (roughly 3-10 monosaccharide molecules) and polysaccharides, which is starch (more than 10 monosaccharides ). These are not very sweet.
If you continue with even longer chains of monosaccharides, you arrive at cellulose. The cellulose chains are so long and robust that most animals can’t digest them. Only cows and other ruminants, and a few other species, have that capacity. We humans use it for paper and paper products.
 So, all carbohydrates work in the same way, then?
So, all carbohydrates work in the same way, then?
Not really. And this is the heart of the matter. Our body can only absorb monosaccharides, so before any carbohydrate longer than one molecule can be of any use to us it has to be broken down. This process happens in the small intestine with the help of enzymes, and the longer the carb chain is, the more the intestine has to work, and the longer it takes.
That’s why diabetics are advised to eat more complex carbohydrates… Vegetables, whole wheat bread, and other stuff with lots of fiber in it. That is also one of the reasons why table sugar is regarded as not as healthy as whole grain. Complex carbohydrate helps control the blood sugar, and it makes the intestine exercise, which is another benefit.
Can you live without sugar?
Yes. Table sugar isn’t necessary, nor is it beneficial.
Can you live without carbohydrates, altogether?
Yes, you can. Because the human body’s gastrointestinal tract is a miracle of flexibility. After all, we are one of the very few species that have spread to every corner of this planet, excluding Antarctica. And we have done so partly because our digestion system is so incredibly adaptable… Which brings us to the Inuit and their very particular diet…
The Inuit and the high-protein diet.

There are certain places on our planet where things just do not grow. One such place is the vast, frozen land around the north pole – Greenland, and the northern parts of Siberia, Alaska, and Canada. The Inuit who live there, are forced, by the climate, to limit their intake of carbohydrates. Instead, their traditional diet consisted almost exclusively of the two other main parts of our food: protein and fat.
According to most diet experts, they should all be high on cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, and cancer. They should have extreme cholesterol levels, and no teeth left after 30, with a high protein diet like that.
But strangely, they seem to be just as healthy as anybody else even though they eat almost no carbs whatsoever. It’s a mystery and has been so for a long time…
The Inuit paradox
So, how can they be so healthy with an almost complete lack of carbs? And we’re back to the extreme capacity for adaptation within the human race.
Harold Draper, biochemist, and expert in Eskimo nutrition:
– There are no essential foods… Only essential nutrients. And humans can get those nutrients from diverse and eye-opening sources.
One big problem with the Inuit diet would be the lack of vital vitamins, present mostly in vegetables, and fruits. But researchers found vitamins in a lot of different animal food sources.
D-vitamins that are produced by the sunlight, are also found in fatty fish.
Fat or sugar? What to choose?
Can you live without sugar for energy?… Fat and carbohydrates are the body’s main energy sources. Fat is for storage, and carbs are for immediate use. Both have their issues, but there’s nothing inherently worse with fat as an energy resource.
And the intuits still eat some carbohydrates. A minimal part of carbs come from the tubers, and berries they pick in summer. Another source is the glycogen present in meat, especially raw meat.
The fantastic evolution of the human body.
For many years, omega 3, a beneficial fatty acid, was considered the reason why the Inuit didn’t die from heart attacks at a greater range. Omega 3 is a known protector against cardiovascular diseases, and the Inuit population has very high levels of omega 3. Even though they eat a lot of protein and fats they are not subject to more heart problems than the rest of us.

But recent studies have discovered a gene, a mutation, found in the Inuit population. This mutation partly counteracts the effects of a diet high in marine mammal fat. Interestingly it is also in some way connected to height. Inuit, in fact, are statistically much shorter than their Canadian, Danish, and Russian peers. This would be another advantage in a cold climate.
Is a complete no-carb diet healthy? … Or even possible?
So, back to my diabetes. Would it be possible to throw all the carbohydrates out the window, and eat only fat and proteins? Can you live without sugar… completely?
It evidently is possible. The fantastic human body, perfected after billions of years of evolution, can take almost anything. It can adapt.
But… And this is maybe the crucial point, would it be good for me, even if I’m a diabetic?
What the scientists say.
There is a clear link between low-carb diets and increased health risks. Many studies have confirmed that. But much like the Inuit, you will have to increase fat and proteins, if you decrease carbohydrates. And there’s also a clear link between eating animal protein, especially red meat, and increased risk for cardiovascular diseases.
So, do you get sicker because you eat fewer carbs, or because you eat more steaks?
However, excluding carbs altogether doesn’t seem like a good idea, unless you’re of Inuit origin.

There is also a clear link between refined sugar and health risks. Maybe the choice shouldn’t be so much between simple and complex carbohydrates, as between refined and non-refined. The sugar in the apple pie is more damaging than the sugar in the apple.
Is a piece of apple pie really all that dangerous?
No, not really. If you eat one piece and stop there. Even a diabetic can eat one small piece of apple pie without any particular consequences. Sweets taste good, and as long as you don’t exaggerate, don’t be too hard on yourself.
There still are a few general propositions about healthy dieting I would like to make. Some basic rules for any diet, anywhere.
- Surviving is different from living for many years. You can survive on whatever for a short period of time, but if the nutrition is incomplete, you risk your long-term health.
- It is always preferable to mix. The more one-sided you eat, the greater the health risk. (So, it’s better to eat fat, protein, AND carbs.)
- Unrefined food is preferable to refined
- Seasonal food is preferable to food that is out of season and maybe imported.
- You can go low on something, low protein, low fat, or low carb. But do not exclude anything. We are built to eat a little of everything. And we need all of it, at least to some degree.
Conclusion.
First, you can and should avoid refined sugar.
Secondly, living completely without or with a limited intake of carbohydrates is possible, that is, you will survive. But unless you are an Inuit or of Inuit origin, it’s unhealthy. And even if you are of Inuit blood, the modern lifestyle and the many easily accessible industrially made foods suggest that a no-carb diet could still be very harmful. Hey, even a low-carb diet should be used with caution.
We just don’t get around it. We need the carbs, at least some of them… Just like we need protein, fat, vitamins, minerals, and all the rest. We are omnivorous.
… And maybe that includes a piece of the apple pie and a small brownie too.
Yes, you can and should live without refined sugar. But to live for an extended period without any carbohydrates? That, I’d say, would be very risky.

- Discover Magazine / The Inuit Paradox
- Angus Chen / The Secret To The Inuit High-Fat Diet May Be Good Genes
- Openheart / The introduction of refined carbohydrates in the Alaskan Inland Inuit diet
- European Society of Cardiology / Low carbohydrate diets are unsafe and should be avoided
- National Library of Medicine / Lower carbohydrate diets
- Berkeley News / What the Inuit can tell us about omega-3 fats and ‘paleo’ diets
- Diabetes.co.uk / Sugar vs Fat
- Wikipedia / Low-Carbohydrate diet




 The final verdict
The final verdict

 A short history of the magical beverage.
A short history of the magical beverage.
 But let’s talk about the energy boost, and that’s mostly linked to Caffeine.
But let’s talk about the energy boost, and that’s mostly linked to Caffeine. What?
What?



 Heinz, and the origin of the American ketchup
Heinz, and the origin of the American ketchup